Validating User Input
The third example shows how the
TRequiredFieldValidator and TEmailAddressValidator work in a form respectively to ensure that a user enters some data in the specified input field and to verify whether the user input is a valid email address.Home.page
<html>
<head><title>Register</title></head>
<body>
<h1>Register</h1>
<p>Please fill out the following form to register on the site.</p>
<com:TForm>
<span>Name:</span>
<com:TRequiredFieldValidator ControlToValidate="name"
ErrorMessage="Please provide your name."
Display="Dynamic" />
<br/>
<com:TTextBox ID="name" />
<br/>
<span>Email:</span>
<com:TRequiredFieldValidator ControlToValidate="email"
ErrorMessage="Please provide your email address."
Display="Dynamic" />
<com:TEmailAddressValidator ControlToValidate="email"
ErrorMessage="You entered an invalid email address."
Display="Dynamic" />
<br/>
<com:TTextBox ID="email" />
<br/>
<span>Password:</span>
<com:TRequiredFieldValidator ControlToValidate="password"
ErrorMessage="Please provide your password."
Display="Dynamic" />
<br/>
<com:TTextBox ID="password" TextMode="Password" />
<br/>
<span>Message:</span>
<com:TRequiredFieldValidator ControlToValidate="message"
ErrorMessage="Please provide a message."
Display="Dynamic" />
<br/>
<com:TTextBox ID="message"
TextMode="MultiLine"
Rows="3"
Columns="20" />
<br/>
<com:TButton Text="Submit" OnClick="ButtonClicked" />
</com:TForm>
</body>
</html>
Home.php
<?php
class Home extends TPage
{
public function buttonClicked($sender,$param)
{
echo '<h1> You have registered successfully on this site! </h1>';
}
}
?>
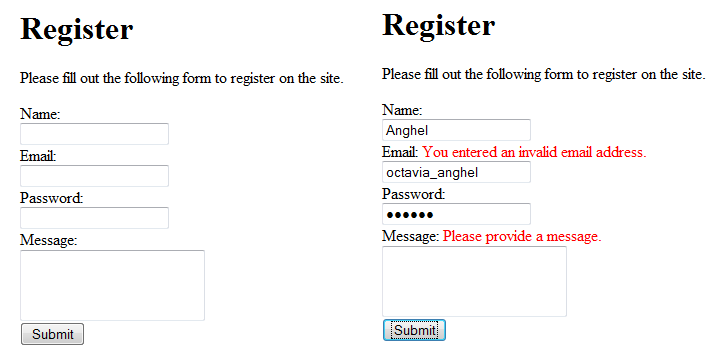
Figure 5 shows how the validators specify that a field is empty and one is invalid.
Click here for larger image
Figure 5. How the TRequiredFieldValidator and TEmailAddressValidator Work
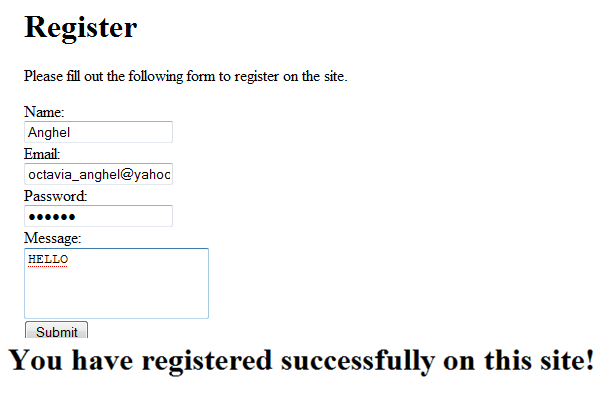
Figure 6 shows when everything was fine and the validators didn’t have to give any message.
Click here for larger image
Figure 6. A Successful Message
Inserting Headers and Footers
The next example shows how to insert a simple header and footer into a page. The header will contain the text “My personal page” and the footer will contain a small picture,
1.jpg.The three new tags used are:
-
<com:TContentPlaceHolder>represents the TContentPlaceHolder control. It reserves the place in the template where content will be placed. Here, the content comes from the pages that use this master control. -
<com:THead>represents the THead control, which is the HTML<head>tag. You can use it to manipulate the<head>tag as a component for setting page titles, adding custom CSS styles, etc. -
<%= %>is an expression tag.
Home.page
<html>
<com:THead />
<body>
<com:TForm>
<div id="page">
<div id="header">
<h3>My personal page </h3>
</div>
<div id="main">
<com:TContentPlaceHolder ID="Main" />
</div>
<div id="footer">
<%= 01.jpg %>
</div>
</div>
</com:TForm>
</body>
</html>
Home.php
<?php
class Home extends TTemplateControl
{
}
?>
Conclusion
In this article you have learned how to implememnt custom components into your PHP 5 applications using the PRADO framework.
For Further Reading
About the Author
Octavia Andreea Anghel is a senior PHP developer currently working as a primary trainer for programming teams that participate at national and international software-development contests. She consults on developing educational projects at a national level. She is a coauthor of the book “XML Technologies — XML in Java” (Albastra, ISBN 978-973-650-210-1), for which she wrote the XML portions. In addition to PHP and XML, she’s interested in software architecture, web services, UML, and high-performance unit tests. to e-mail her.